Amoxicillin is a well-known antibiotic that plays a vital role in treating a diverse range of bacterial infections. This article provides an in-depth exploration of amoxicillin, its uses, potential side effects, and important considerations for its usage.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Amoxicillin: An Overview
- Common Infections Treated by Amoxicillin
- How Does Amoxicillin Work?
- Understanding Amoxicillin’s Mechanism of Action
- Mild and Common Side Effects
- Dealing with Mild Side Effects
- Serious but Rare Side Effects
- Allergic Reactions and Immediate Medical Attention
- Seizures and Special Precautions
- Liver and Kidney Health Concerns
- Pseudomembranous Colitis: A Serious Complication
- Other Uncommon Side Effects
- When to Seek Medical Assistance
- Proper Administration of Amoxicillin
- Taking Amoxicillin with Care
- Storing Amoxicillin Safely
- Handling Amoxicillin Overdose
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
Amoxicillin, a widely prescribed antibiotic, stands as a stalwart defender against various bacterial infections. Its versatility in addressing numerous ailments makes it a vital component of modern medicine.
Amoxicillin: An Overview
Amoxicillin belongs to the penicillin family of antibiotics and is renowned for its effectiveness in combating bacterial infections. Its spectrum of activity encompasses ailments like ear infections, sinus infections, strep throat, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, gonorrhea, Lyme disease, and salmonellosis.
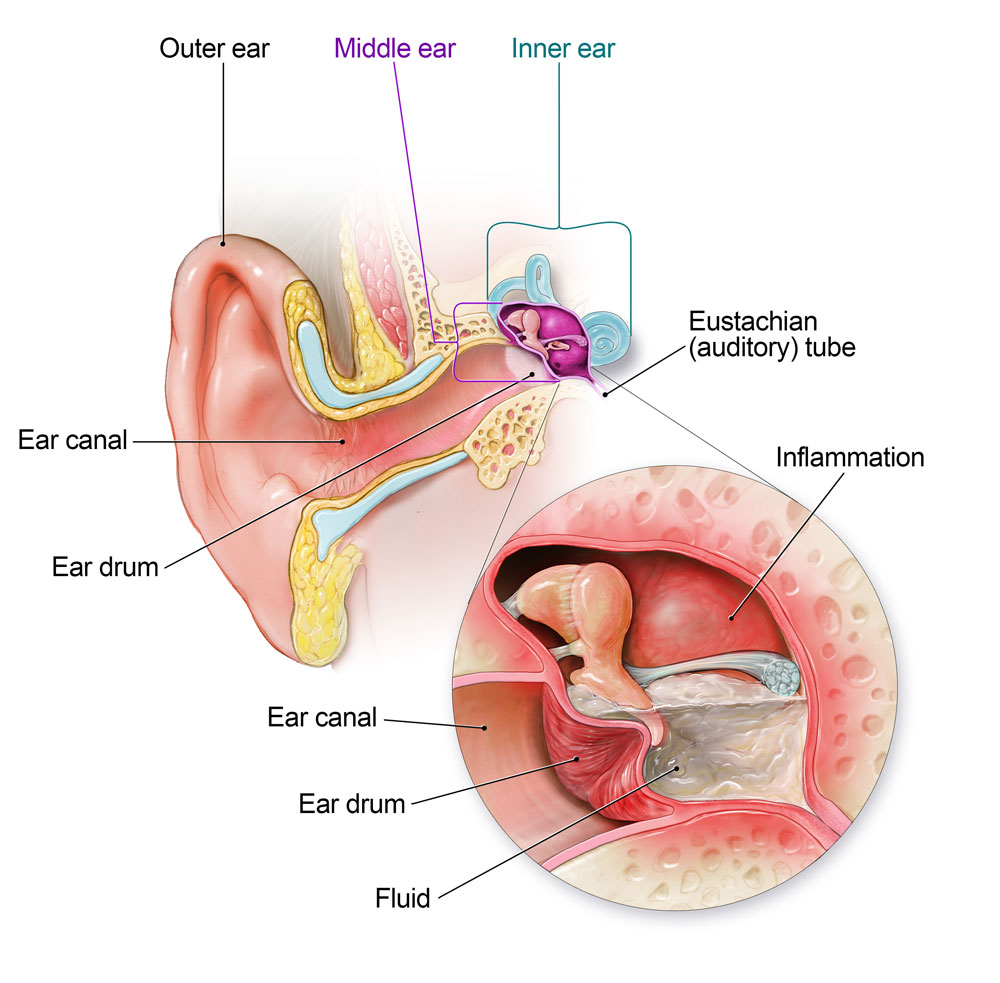
Common Infections Treated by Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin’s utility spans across a plethora of conditions, including:
- Ear infections
- Sinus infections
- Strep throat
- Pneumonia
- Urinary tract infections
- Gonorrhea
- Lyme disease
- Salmonellosis

How Does Amoxicillin Work?
Understanding amoxicillin’s mechanism of action sheds light on its efficacy. By disrupting bacterial cell wall synthesis, it renders the bacteria defenseless and unable to survive.
Understanding Amoxicillin’s Mechanism of Action
At the core of amoxicillin’s effectiveness is its disruption of bacterial cell wall formation. This vital structure maintains the integrity of bacteria, and without it, they meet their demise.
Mild and Common Side Effects
While generally well-tolerated, amoxicillin can induce mild side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, upset stomach, loss of appetite, rash, hives, itching, headache, dizziness, and fatigue.
Dealing with Mild Side Effects
The majority of mild side effects are transient and subside with time. Should they persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable.
Serious but Rare Side Effects
Although infrequent, amoxicillin can trigger severe side effects, including allergic reactions, seizures, liver damage, kidney damage, and pseudomembranous colitis.
Allergic Reactions and Immediate Medical Attention
An allergic reaction demands swift action. Symptoms like hives, swelling, breathing difficulties, and shock necessitate immediate discontinuation of amoxicillin and medical attention.
Seizures and Special Precautions
Seizures, though rare, merit special consideration. Individuals with kidney issues or a history of seizures should consult their healthcare provider before commencing amoxicillin.
Liver and Kidney Health Concerns
Amoxicillin’s impact on the liver and kidneys underscores the need for caution. Vigilance for symptoms like yellowing of the skin, dark urine, nausea, and more is crucial.
Pseudomembranous Colitis: A Serious Complication
Pseudomembranous colitis, a severe condition causing colon inflammation, demands attention if symptoms like watery diarrhea and abdominal cramps arise.
Other Uncommon Side Effects
Amoxicillin’s spectrum of effects includes rare occurrences such as chest pain, chills, joint or muscle pain, tooth staining, and more.
When to Seek Medical Assistance
Prompt medical consultation is warranted for serious side effects, persistent or new side effects, and concerns about side effects.
Proper Administration of Amoxicillin
Following prescribed guidelines for amoxicillin administration is pivotal. Proper dosage and compliance ensure optimal efficacy.
Taking Amoxicillin with Care
Taking amoxicillin with food minimizes stomach discomfort. Straying from prescribed dosages or durations should be avoided.
Storing Amoxicillin Safely
Storing amoxicillin in a cool, dry place at room temperature ensures its potency. Keeping it out of children’s reach is essential.
Handling Amoxicillin Overdose
Overdosing on amoxicillin can have grave consequences like seizures, liver damage, and kidney damage. Immediate medical attention is imperative.

Conclusion
Amoxicillin’s significance in treating bacterial infections cannot be overstated. While it bestows remarkable benefits, understanding its potential side effects empowers individuals to use it responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can amoxicillin cause allergic reactions? A: Yes, amoxicillin can trigger allergic reactions, which should be treated as a medical emergency.
Q2: Is amoxicillin safe for people with kidney issues? A: People with kidney problems should consult their doctor before taking amoxicillin.
Q3: What should I do if I experience severe side effects? A: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe side effects or symptoms you are concerned about.
Q4: How should amoxicillin be stored? A: Amoxicillin should be stored in a dry place at room temperature, away from children.
Q5: Can amoxicillin be taken without a prescription? A: No, amoxicillin requires a prescription from a healthcare professional.